Incontinence Most Recent
Urinary incontinence is a prevalent condition among long-term care residents, particularly those with dementia. The costs and morbidity associated with urinary incontinence are significant.
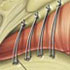
Urinary incontinence is a significant problem in older women. Prevalence rates vary from 4.5–44% in healthy older women and increase to 22–90% in patients in long-term care facilities.
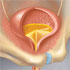
Urinary incontinence, the involuntary loss of urine, is a common medical condition in the elderly. Over 1.5 million Canadians are currently afflicted with the condition, and the number is expected to increase significantly over the next 20 years as the baby boom population ages.
The human body undergoes important physiological changes as it ages and the urinary system is no exception to this trend.
Urinary incontinence can be successfully treated in some individuals. There are, however, many individuals who remain unresponsive to behavioural, medical or surgical treatment and continue to experience chronic urinary incontinence.
Functional urinary incontinence is one of five types of incontinence. The assessment and therapeutic interventions associated with functional incontinence are reviewed in this fifth and final article of a five part series on urinary incontinence.
Advertisement
Overflow urinary incontinence is one of five types of incontinence. The assessment and therapeutic interventions associated with overflow incontinence are reviewed in the fourth article of a five-part series on urinary incontinence.
Urge urinary incontinence is one of five types of incontinence. The assessment and therapeutic interventions associated with urge incontinence will be reviewed in this third article of a five-part series on urinary incontinence.
Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is one of five types of incontinence. The assessment and therapeutic interventions associated with stress incontinence will be reviewed in this second article of a five-part series on Urinary Incontinence.
Prevalence studies of urinary incontinence in the elderly report widely-varying rates from 4.5-44% in healthy, elderly women to 4.6-24% in healthy, elderly men. The prevalence in institutionalized people ranges from 22-90%.
